Setup Optic in CI
Prevent breaking changes from landing in production, keep your documentations up-to-date and enforce API governance by adding Optic to your CI pipelines.
1. Set up Optic in CI
Get your organization OPTIC_TOKEN from the webapp (opens in a new tab) in the Tokens tab.
Github
name: optic
on:
pull_request:
push:
branches:
- "main"
jobs:
run:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Install Optic
run: npm install --location global @useoptic/optic
- name: Run Optic
env:
OPTIC_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.OPTIC_TOKEN }}
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
run: optic runGitlab
Don't forget to add the OPTIC_TOKEN and OPTIC_GITLAB_TOKEN variables to your workflow.
optic-default-branch-push:
image: node:latest
rules:
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "push" && OPTIC_TOKEN && $CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME == $CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH
script:
- npm install -g @useoptic/optic
- optic run
optic-merge-request:
image: node:latest
rules:
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "merge_request_event" && $OPTIC_TOKEN
script:
- npm install -g @useoptic/optic
- export OPTIC_RESULT=0; optic run || export OPTIC_RESULT=$?
- if [ $OPTIC_RESULT -ne 0 ]; then exit 1; fi;Configure commenting on Pull Requests (optional)
Optic posts a summary of the run as a comment on pull / merge requests when there is something meaningful to report.

Github
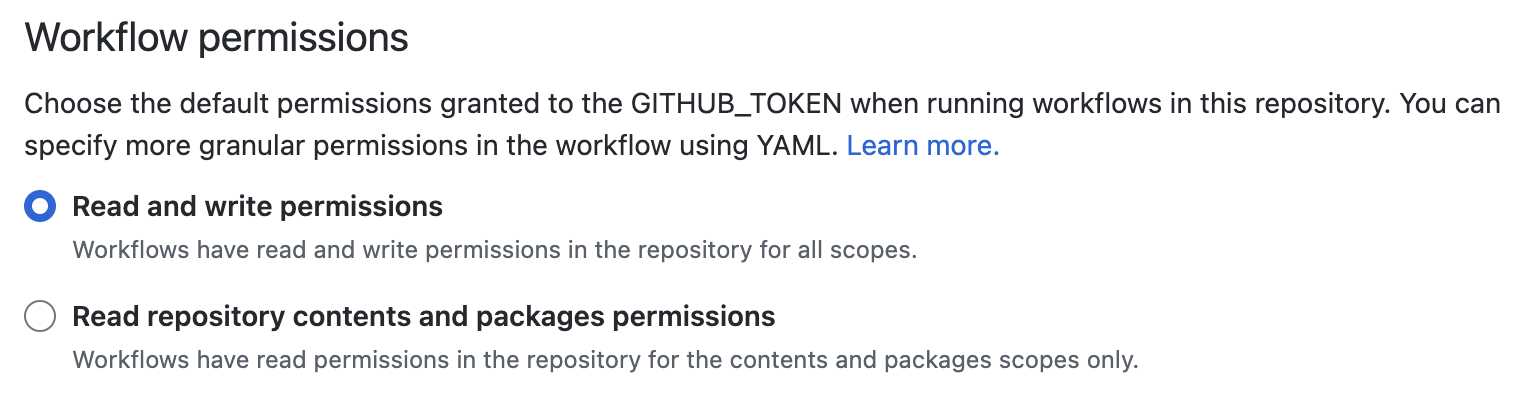
Navigate to Repo > Settings > Actions > General and set Workflow permissions to Read and write permissions.
Gitlab
Give the Optic Pipeline an OPTIC_GITLAB_TOKEN variable containing a token with the api scope to setup Optic comments on your pull requests. When setting up the variable, uncheck the "Protect variable" option to let Optic run on your MRs.
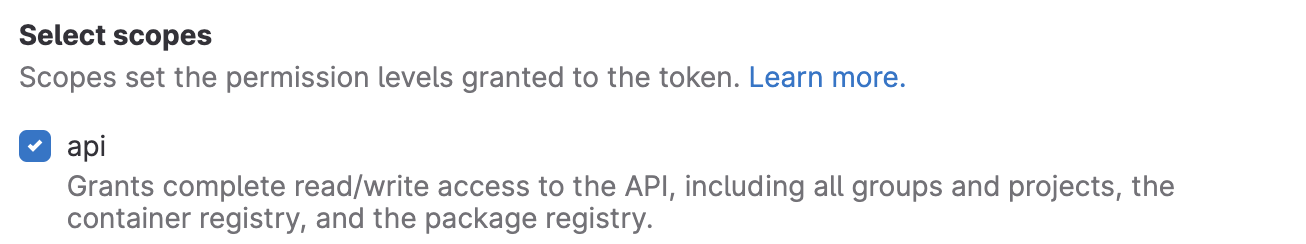
When creating the token, select the api scope:
When adding the variable to the project, uncheck the protect variable option:

We strongly recommend using a Group Access Token (opens in a new tab):
- it is what GitLab recommends
- comments will come from a group bot, not your personal account
- the same token can be used across all the projects in a group
2. Trigger Optic
Now that we've set up everything, it's time to test out the entire flow! Ensure that all the changes in the previous steps have been merged into your main branch.
Make some changes
Start by making a pull request and making a couple of changes to your API. Below are some suggestions of changes:
- Remove an endpoint
- Remove a field from a response body
- Add a required query parameter to an endpoint
Notice anything about these changes? These are breaking changes that Optic is designed to prevent!
See how Optic works
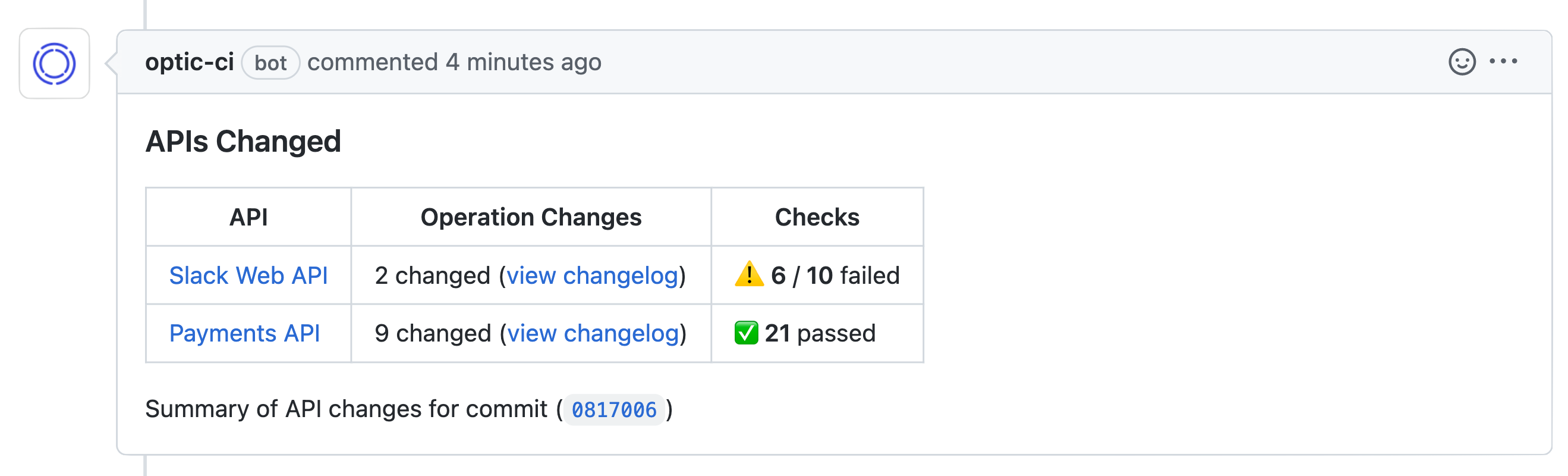
You should notice once you open your PR, Optic will diff changes between the main branch and the pull request's branch and post a comment once it's completed with:
- The results of any automated checks
- A link to preview your documentation (Optic cloud only)
- A link to the proposed changes in the PR (Optic cloud only)
Troubleshooting
Didn't get a pull request comment from Optic or something didn't quite work right? Here's some common troubleshooting steps:
- Is the Optic workflow being triggered in CI?
- Does the workflow have the
Read and write permissionsenabled?
What's next?
Congratulations, Optic is now set up to track all changes and run automated checks against every API change.
Did you know you could configure your standards? Check the standards documentation for a detailed view of Optic capabilities.